Injection molding is a process of manufacturing products using molds. Materials such as metals and plastics are heated, melted, and fed into the mold, left to cool, solidify and take shape. The process is called injection molding because it’s similar to injecting fluids using a syringe.
This is how the process works: First, the materials are melted and fed into the mold, where they solidify, and the products are extracted and finished. With injection molding, you can continuously manufacture different parts, including those with intricate shapes in large volumes. Hence, injection molding is used to manufacture products or items across various industries in high volume.
Table of Contents
Injection Molding Machines
Injection molding machines are available in different types, they include:
- Motorized machines driven by servo motors
- Hydraulic machines are driven by hydraulic motors and h
- A servo motor and a hydraulic motor drive hybrid machines.
The structure of an injection molding machine can be described as a machine made up of an injection unit that feeds melted materials into the mold and a clamping unit used for operating the mold.
Recently, injection molding machines have included CNC, which has opened the floor for other models that enable high-speed injection under programmed control. On the flip side, some specialized machines are also used, for instance, models that form the light guide plates for LCD monitors.
Basic Structure of Injection Molding Machines
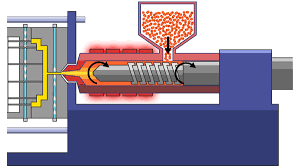
- Cylinder (heats the material)
- Nozzle (injects the melted material)
- Hopper (material feeder)
- Mold (material is poured into the mold cavity between two plates)
Injection Molding Process
Injection molding starts with resin pellets being fed into the hopper, which is the entrance for the material. The pellets are then heated and dissolved inside the cylinder as they get prepared to be sent through the injection unit. The material is then used through the nozzle of the injection unity before it passes through another channel in the cavity called sprue and through branched runners and finally stops in the mold cavity. This is where the material is left to cool and solidify, after which the mold opens, and the molded part is pushed out of the mold. To finish the molded part, the sprue and runner are removed from the product or item.
The melted materials needed to produce a part need to be spread out evenly in the mold because there’s usually more than one cavity in the mold, and the material needs to fill every part up to produce more than one part at a time. Therefore when designing the mold shape, it should have less complicated designs, and if possible, the runners should be of the exact dimensions.
Before you consider using the injection molding process for the mass production of your items, you must understand the factors and conditions required for producing high-quality products. These conditions include choosing the best resin material, the processing and accuracy of the mold, and the speed and temperature of the melt injection.