Energy-efficient and sustainable heating and cooling technologies have received more attention in recent years. Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs) are a technology that has received a lot of interest. GSHPs use the natural energy that is underground to efficiently heat, cool, and produce hot water for both residential and commercial buildings. In this post, we’ll look at how employing sensible tactics can help you get the most out of ground source heat pumps’ energy efficiency.
Understanding Ground Source Heat Pumps
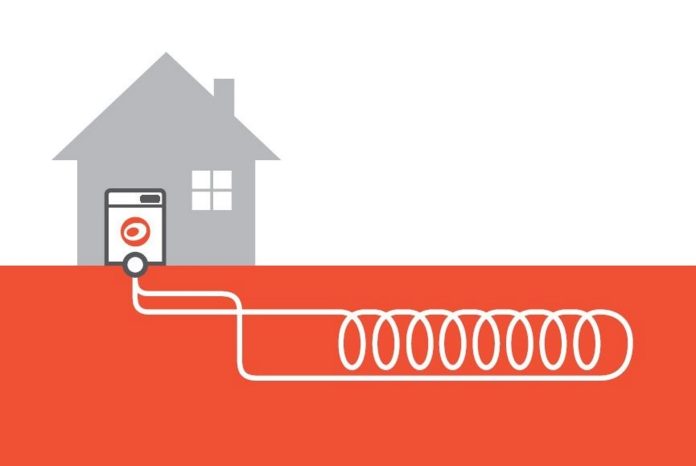
Let’s take a quick look at how ground source heat pumps function before moving on to increasing energy efficiency. The earth’s constant temperature is used by GSHPs to transmit heat from the ground to a building. The distribution system, heat pump unit, and ground loop make up their three primary parts.
A heat transfer fluid runs through a network of pipes that make up the ground loop, which is buried beneath. When this fluid is in the heating phase, it draws heat from the ground and releases it when it is in cooling mode. The heat pump unit, which is inside the structure, pulls heat from the ground loop and transmits it to the distribution system, which might be forced air, radiators, or underfloor heating.
Let’s now examine useful tips for GSHP energy efficiency maximisation:
- Proper Sizing and Design
To maximise energy efficiency, it is essential to make sure the GSHP system is scaled and configured correctly. Systems that are too small may have trouble keeping up with heating or cooling demands, which may impair efficiency and increase energy use. Conversely, oversized systems have a tendency to often cycle on and off, wasting energy.
Determine the proper size depending on elements like building size, insulation levels, and climate conditions by working with a certified HVAC professional or engineer with experience in GSHP systems. They are able to calculate the heat load to precisely size the system and plan the ground loop structure for maximum effectiveness.
- Efficient Ground Loop Design
For GSHPs to operate effectively and use less energy, the ground loop’s design is essential. Considerations include the following:
Horizontal vs. Vertical Loops:
The ground loop system’s design is extremely important for maximising the energy efficiency of ground source heat pumps (GSHPs). The decision between horizontal and vertical loops is an important one to take into account. When there is enough room, horizontal loops are frequently employed because trenches can be dug to fit the loop configuration.
They can offer effective heating and cooling while being easier and less expensive to install. Vertical loops, on the other hand, are appropriate for properties with a limited amount of space because they require digging deep boreholes. Although vertical loops demand a larger initial investment, they have the benefit of maintaining a steady ground temperature at longer depths, which improves energy efficiency.
Depending on site-specific elements, including accessible land area, geological circumstances, and financial constraints, horizontal or vertical loops may be preferred. You can guarantee the best energy performance and financial savings for your GSHP system by working with knowledgeable ground loop design specialists.
Proper Sizing and Configuration
Based on the building’s heating and cooling needs, the ground loop must be sized suitably. To maximise heat exchange with the earth, suitable configurations must also be taken into account, such as loop length and spacing.
Thermal Conductivity
Achieve good thermal contact between the ground loop and the surrounding soil. Better heat transmission and increased system efficiency result from higher thermal conductivity.
- Insulation and Building Envelope
Insulation and the building envelope are equally important in maximising the energy efficiency of ground source heat pump (GSHP) systems as proper sizing and configuration. Buildings with good insulation minimise heat gain or loss, which lowers the total demand on the GSHP system.
The GSHP can function more effectively by maintaining a constant internal temperature with enough insulation in the walls, roofs, and floors. Similarly, a properly sealed building envelope reduces energy losses and guarantees the GSHP system can successfully maintain desired temperatures by preventing air leakage. Property owners can improve the efficiency of their GSHP system and obtain maximum energy performance by giving insulation and building envelope modifications first priority.
In order to maximise the effectiveness of the entire system, consulting with energy efficiency specialists or licenced GSHP installers can offer helpful insights into efficient insulation measures and building envelope changes.
Insulation:
For walls, roofs, floors, and windows, use high-quality insulating materials to reduce heat transfer. To avoid gaps and thermal bridges, make sure the installation is done correctly.
Air Sealing:
Sealing air leaks will stop draughts and heat loss. Apply the required weatherstripping or sealants after checking for air leaks in windows, doors, vents, and ducts.
- Efficient Heat Pump Operation
Energy efficiency can be considerably increased by optimising the performance of the heat pump equipment itself:
Programmable Thermostats:
To modify temperature settings based on occupancy and schedule, use programmable thermostats or smart controls. By doing so, unwanted heating and cooling are avoided, and energy use is decreased.
Maintenance and Filter Cleaning:
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to maintain the heat pump system on a regular basis. Filters should be cleaned or changed as needed to ensure adequate airflow and system effectiveness.
- Renewable Energy Integration
To further improve energy efficiency, think about integrating renewable energy sources into your GSHP system:
Photovoltaic (PV) Systems:
Install solar cells to produce the electricity needed to run the GSHP system. Overall energy use can be decreased by balancing the power used by the heat pump with the renewable energy produced.
Wind Turbines:
Wind turbines may also be utilised in the right locations to power GSHPs. Utilising wind energy increases sustainability and lessens reliance on the grid.
With ground source heat pumps, you can increase energy efficiency by using these achievable tactics. This will contribute to more sustainable and environmentally friendly construction in addition to lowering energy expenses. Enjoy the advantages of effective heating and cooling with GSHPs by consulting industry experts to secure the best outcomes for your unique application.